What is a Watershed?
A watershed is an area of land that water flows across, through, or under on its way to a common point in a stream, river, lake, or ocean. Watersheds not only include water bodies such as streams and lakes, but also all the surrounding lands that contribute water to the system as runoff during and after rainfall events. The relationship between the quality and quantity of water affects the function and health of a watershed. Thus, significant water removals (such as irrigation) or water additions (such as permitted discharges) are important.

Watersheds can be extremely large, covering many
thousands of acres, and often are subdivided into smaller sub-watersheds for the purposes of study and management.
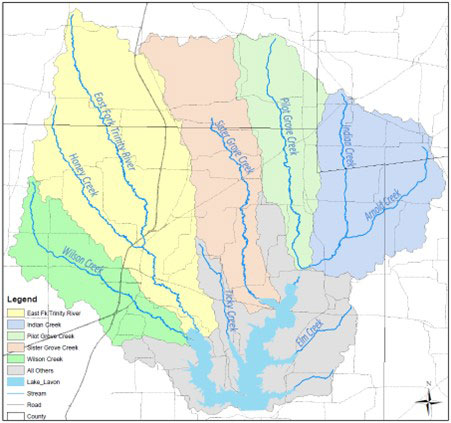
The Lavon Lake Watershed is the uppermost reservoir on the East Fork of the Trinity River. This watershed is the primary source of raw water supply for the North Texas Municipal Water District and over 1.6 million North Texas residents rely on Lavon Lake as their primary source of water. There were two tributaries to the Lavon Lake Watershed that were identified as impaired due to elevated levels of E. coli bacteria in 2014. Nonpoint source pollution occurs as water moves through the watershed and picks up natural and human-related pollutants and deposits them into water bodies such as creeks, rivers, and lakes.