Front Page
-
Texas Star, 1932. Briscoe-Garner Museum Quilt Collection. The Dolph Briscoe Center for American History is pleased to announce the quilt exhibit Citizen Stitching: Political Quilts in the Winedale Quilt Collection. The exhibit will be on display from July 15 through July 27, 2024, at the Sam Rayburn Museum, a division of the Briscoe Center in Bonham, Texas. The exhibit coincides with the 2024 Bonham Quilt Hop on Friday, July 26, and Saturday, July 27, from 10:00 a.m. to 4:00 p.m.
-
Previous celebrations have brought large turnouts to the Choctaw Cultural Center. On Saturday, July 27 the Choctaw Cultural Center will mark its third anniversary with a full slate of activities for the whole family. The public is invited for a day of activities for all ages from 10:00 a.m. to 4:30 p.m. photo provided by the Choctaw Nation
-
Don't miss out on this incredible celebration of quilting arts. Whether you're here to learn, play, shop, or simply admire the craftsmanship, the 2024 Bonham Quilt Hop offers something for everyone. Pack your bags, bring your quilting spirit, and get ready to hop from one magical location to another. See you in Bonham!
-
Join us for an evening of fun and investigation as we celebrate National Moth Week! Equipped with gentle light features to attract them, we'll explore the hidden beauty of moths and other nocturnal creatures. This unique event offers an unforgettable look at nature's most captivating night-time creatures. See the night as you’ve never seen it before! Pre-registration is required.
-
SMU and the University of Rhode Island have patented an inexpensive, easy-to-use method to create solid-state nanopores (SSNs), while also making it possible to self-clean blocked nanopores.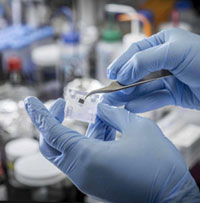
-
1890 – Vincent van Gogh shoots himself and dies two days later. Vincent Willem van Gogh (30 March 1853 – 29 July 1890) was a Dutch Post-Impressionist painter who is among the most famous and influential figures in the history of Western art. In just over a decade, he created approximately 2100 artworks, including around 860 oil paintings, most of them in the last two years of his life. His oeuvre includes landscapes, still lifes, portraits, and self-portraits, most of which are characterized by bold colors and dramatic brushwork that contributed to the rise of expressionism in modern art. Van Gogh's work was beginning to gain critical attention before he died from a self-inflicted gunshot at age 37. During his lifetime, only one of Van Gogh's paintings, The Red Vineyard, was sold. Van Gogh's work gained widespread critical and commercial success in the following decades, and he has become a lasting icon of the romantic ideal of the tortured artist. Today, Van Gogh's works are among the world's most expensive paintings ever sold.

















